
What is Epoxy and What is Epoxy Flooring?
1. What is Epoxy?
Epoxy refers to a class of organic compounds where an oxygen atom is inserted into a carbon chain. The most common example is ethylene oxide (CH₂-O-CH₂), where two carbon chains are connected by an oxygen atom, forming a triangular ring structure.
2. What is Resin?
Resin typically describes an organic polymer that softens or melts within a specific temperature range. When softened, it can flow under pressure. At room temperature, resins are usually solid or semi-solid, though some can be liquid.
A common everyday example of resin is eyeglass lenses, prized for their impact resistance (´・ω・)ノ
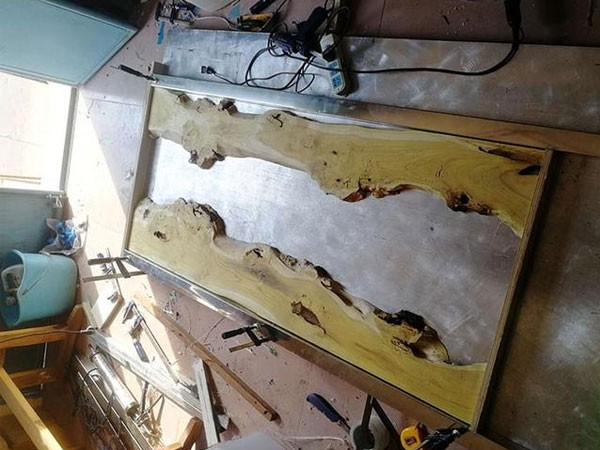
3. What is Flooring (or a Floor System)?
A flooring system, or industrial floor, involves treating an existing concrete subfloor with specific materials and techniques to achieve a decorative and functional surface. Think of it like road construction: to create a smooth road surface, compactors are used.

After treatment, the road becomes level, reducing bumps for trucks.
In earlier times or in less developed settings, roads might be simple compacted dirt or gravel. However, such surfaces aren't water-resistant or durable—you could chip a piece off with a knife. With more resources, a layer of Asphalt Concrete (blacktop/tarmac) is typically added for waterproofing and wear resistance! Roads are among the most common examples of a functional flooring system.

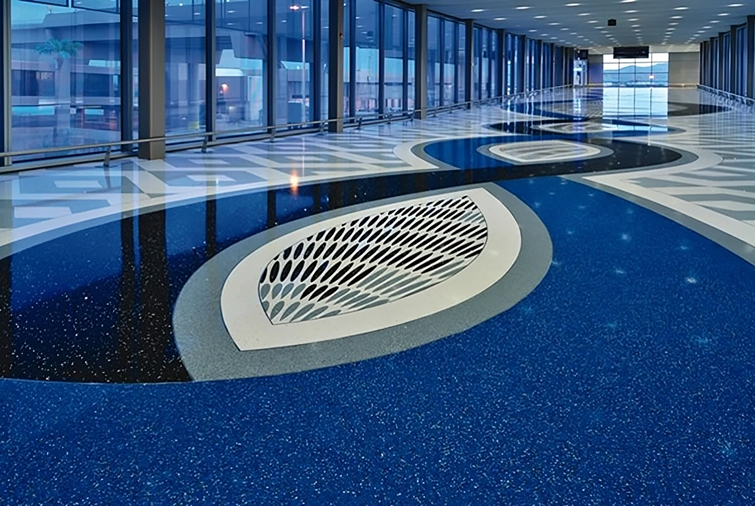
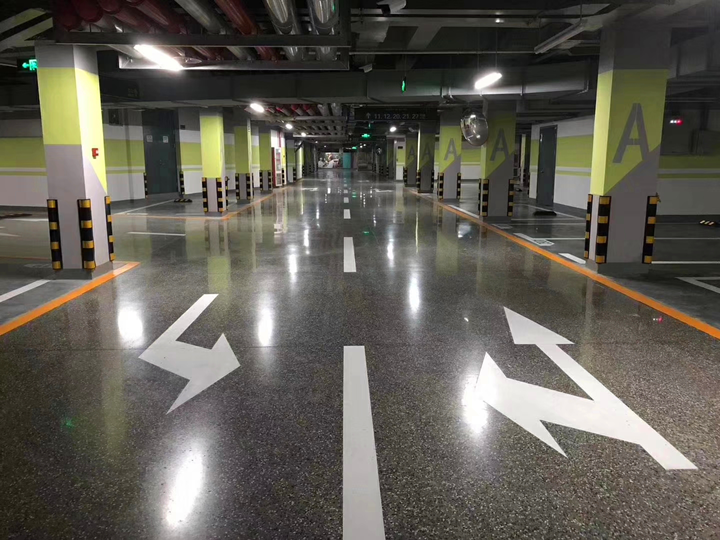
4. What is Epoxy Flooring?
Epoxy flooring is a high-strength, wear-resistant, and aesthetically pleasing floor coating. Before its advent, marble tiles, ceramic tiles, and plain concrete were widely used. However, tiled floors have grout lines that are difficult to clean, and replacing a single broken tile is troublesome. Plain concrete, while inexpensive and initially popular in workshops, is not water-resistant or very durable. Over time, it suffers significant wear.
This led to the invention of hardened industrial floors. Two common types are:
- Concrete Sealers/Hardeners: These penetrate the concrete surface, reacting with calcium compounds to form a sealing gel that fills pores, reducing dust and improving chemical resistance.
- Metallic Aggregate Toppings (e.g., Steel-Reinforced Topping): Alloy powders (often metallic aggregates) are evenly broadcast onto fresh concrete and troweled in, creating an extremely wear- and pressure-resistant surface.
These treatments make floors not just durable, but extremely durable. However, such extreme durability is often unnecessary, and these floors prioritize function over aesthetics, typically lasting 10-20 years.


As needs evolved, demand grew for a floor that was visually appealing, suitably durable, and offered good overall performance. Enter epoxy flooring.
Epoxy resin can be specially formulated into epoxy coatings. Applying these coatings to a floor creates an epoxy flooring system. The process is straightforward in principle: the concrete base is cleaned and profiled (e.g., by grinding), and then the coating is applied (by roller, squeegee, etc.). (How to Epoxy a Garage Floor)

"Coating" is essentially paint. Since paint comes in many colors, is the problem solved? Not quite. Let's recall a chemistry principle:
"Like dissolves like." Organic substances dissolve in organic solvents, inorganic in inorganic.
As established, epoxy resin is organic. Therefore, traditional epoxy coatings (epoxy flooring paint) used organic, oil-based solvents.
This made them flammable, gave them a strong pungent odor, and released significant volatile organic compounds (VOCs).
Epoxy flooring offers many advantages:
seamless, robust, excellent chemical resistance,Wear-resistant, anti-corrosive, dust-proof, easy to clean, and low maintenance cost.
Consequently, it's widely used in factories, server rooms, warehouses, laboratories, hospital wards, operating rooms, and workshops. Through special formulations, epoxy floors can be enhanced for specific physical or chemical properties, achieving functions like corrosion resistance, heavy load-bearing capacity, or static dissipation.
So, what are the drawbacks?
First,it can be scratched—applying firm pressure with a knife can leave a mark (though making a habit of knife-testing floors is questionable). Second, it has limited heat resistance. In an epoxy-floored parking garage, a car turning or braking sharply can generate enough tire heat to leave unsightly black scorch marks.
However, these issues often aren't deal-breakers. If the surface is damaged, it can often be repaired with a fresh coat, sometimes using less than a full bucket of paint. The key is to find a reliable flooring contractor (:3 」∠)








